PTEN p.Ile135Leu Variant: Implications in Neurodevelopmental Disorders
The PTEN p.Ile135Leu (I135L) variant is a mutation in the PTEN gene, where isoleucine is replaced by leucine at position 135. This mutation has been closely associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, particularly autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) accompanied by macrocephaly.
The Role of the PTEN Gene
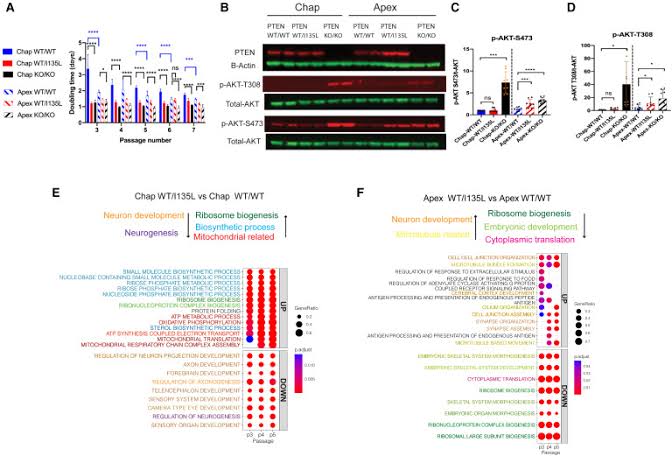
The PTEN gene is crucial for regulating cell growth and division through its role in the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mutations in PTEN, such as p.Ile135Leu, can lead to dysregulated signaling, resulting in abnormal brain development and neurogenesis.
Research Insights by Dr. Anthony Wynshaw-Boris
Dr. Anthony Wynshaw-Boris, a leading geneticist at Case Western Reserve University, has conducted pioneering research on the PTEN p.Ile135Leu mutation. His findings highlight the following:
Impact on Cortical Neurogenesis
- The PTEN p.Ile135Leu mutation disrupts the normal development of cortical neurons in individuals with ASD.
- Using iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and cortical organoid models, Dr. Wynshaw-Boris demonstrated that this mutation results in an overproduction of NPCs and various neuronal subtypes, particularly in an ASD genetic context.
Dysregulated PI3K/AKT Signaling
- The mutation is linked to hyperactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, a key driver of the neurodevelopmental abnormalities observed in ASD patients.
- This dysregulation contributes to the overgrowth of neural cells, which may explain the association of PTEN mutations with macrocephaly.
Significance of Genetic Context
Dr. Wynshaw-Boris’s work emphasizes that the genetic background of an individual modulates the effects of the PTEN p.Ile135Leu mutation. This highlights the need for a personalized approach to understanding the mutation’s role in neurodevelopmental disorders.
Implications for Future Research and Treatment
- Personalized Medicine: The findings stress the importance of tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles.
- Potential Therapeutic Targets: Understanding how the mutation affects PI3K/AKT signaling could lead to the development of targeted therapies for neurodevelopmental disorders.
Conclusion
The PTEN p.Ile135Leu variant offers critical insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying ASDs and related conditions. The groundbreaking research led by Dr. Anthony Wynshaw-Boris underscores the complexity of these disorders and the importance of integrating genetics into personalized approaches for diagnosis and treatment.
Post Comment